Monostage centrifugal extractor
Two immiscible liquids of different densities are fed to the separate inlets and are rapidly mixed in the annular space between the spinning rotor and stationary housing. The mixed phases are directed toward the center of the rotor by radial vanes in the housing base. As the liquids enter the central opening of the rotor, they are accelerated toward the wall. The mixed phases are rapidly accelerated to rotor speed and separation begins as the liquids are displaced upward. A system of weirs at the top of the rotor allow each phase to exit the rotor where it lands in a collector ring and exits the stage. Flow from between stages is by gravity with no need for inter-stage pumps. The centrifugal contactors thus acts as a mixer, centrifuge and pump. Centrifugal contactors are typical referred to by the diameter of their rotor.
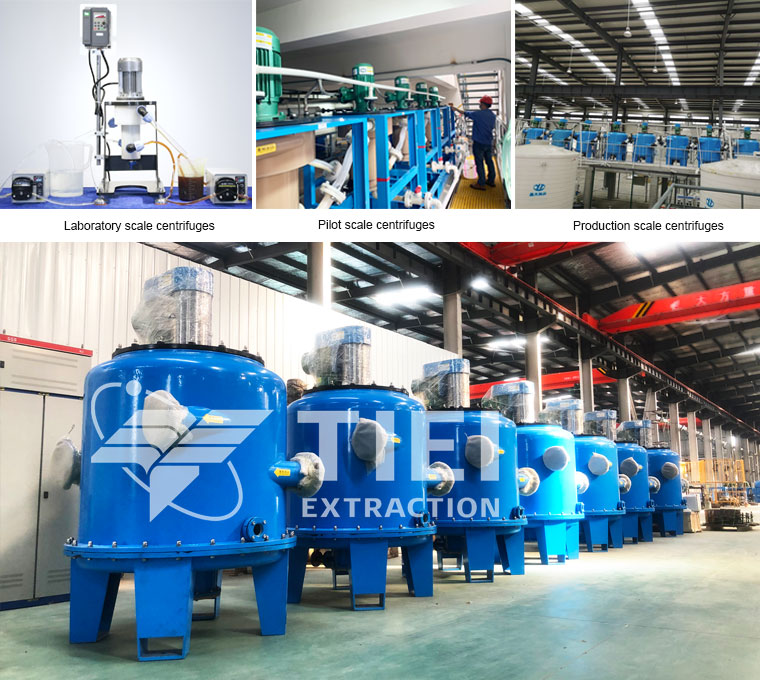

Multistage centrifugal extractor
The feed solution initially containing one or more solutes, and an immiscible solvent having a different density flow counter-currently through the extractor’s rotor, designed with a stack of mechanical subassemblies representing the required number of separate stages. The successive mixing and separation operations performed in each mechanical stage permit the mass transfer of the solutes from the feed solution to the solvent.
Each stage consists of
Mixing chamber where the two phases are mixed and where the transfer of solutes to be extracted is achieved. A fixed disk allows the two phases to be mixed and to create an emulsion. It operates as a pump to draw the two phases from the preceding stage.
Decantation chamber where the two previously mixed liquids are thoroughly separated by centrifugal force. Overflow weirs stabilize the separation area independently of flow rates. The interphase position depends on the diameter of the heavy phase overflow weir, which is interchangeable and to be selected according to the phase density ratio.
Mix and separation
The mix & separation configuration is the standard operation for centrifugal contactors used for liquid-liquid extraction processes. The two liquids enter the annular mixing zone where a liquid-liquid dispersion is formed and extraction occurs as solutes are transferred from one phase into the other. Inside the rotor, the liquids will be separated into a heavy and a light phase by their respective densities. This proportion of each phase, total flow rate, rotor speed, and weir sizes are varied to optimize separation efficiency. The separated liquids are discharged without pressure and flow by gravity to exit the stage.
Tiei Extraction recommends the CWL-M centrifugal extractor ,with detailed equipment specifications and production capacity, technological process, and equipment characteristics. Also you can view relevant customer cases, extraction Technology solutions, and research trends. Browse all extraction equipment.