Benzoic acid, as an important organic acid, is widely used in food preservation, pharmaceutical synthesis, and the production of chemical intermediates. However, benzoic acid–containing wastewater generated during its production, if not effectively treated, can lead not only to resource wastage but also to environmental pollution. Owing to its advantages of high mass-transfer efficiency, rapid phase separation, and low energy consumption, centrifugal extraction technology has become an ideal solution for the recovery and purification of benzoic acid from aqueous systems. This article describes the process flow of benzoic acid separation by centrifugal extraction and, in combination with the technical characteristics of centrifugal extraction technology, discusses its innovative value in industrial applications.
Process Flow for the Separation of Benzoic Acid from Water by Centrifugal Extraction Technology
The solubility of benzoic acid in water varies significantly with temperature, and at ambient conditions it often forms low-concentration organic wastewater. Centrifugal extraction enables efficient recovery of benzoic acid through directed mass transfer and rapid phase separation between two immiscible liquid phases. The core process can be divided into the following four steps:
1.Pretreatment and Extractant Selection
Benzoic acid–containing wastewater is first subjected to filtration or sedimentation to remove suspended solids, thereby preventing blockage of the extraction equipment. The selection of extractants must consider both the distribution coefficient of benzoic acid and the water solubility of the extractant. Commonly used systems include tributyl phosphate (TBP)–kerosene, trialkylamine (N235)–sulfonated kerosene, etc. These extractants exhibit high selectivity toward benzoic acid and enable efficient extraction under low acidity conditions.
2.Multistage Countercurrent Extraction
The wastewater and extractant contact each other in a countercurrent mode within the centrifugal extractor. The high centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation (typically 500–2000 g) rapidly disperses the two phases and forms micron-scale droplets, greatly increasing the interfacial area for mass transfer. Benzoic acid molecules are transferred from the aqueous phase to the organic phase, and after multistage extraction, the benzoic acid concentration in the treated wastewater can be reduced to below 0.1 g/L, while the benzoic acid content in the loaded organic phase can reach 15–25%.
3.Stripping and Benzoic Acid Recovery
The loaded organic phase is contacted with a dilute alkaline solution (e.g., NaOH), converting benzoic acid into water-soluble sodium benzoate, which is transferred back into the aqueous phase. At this stage, the centrifugal extractor achieves rapid separation of the organic and stripping phases by adjusting the rotational speed and phase flow ratio. The stripped organic phase can be regenerated and recycled, while the sodium benzoate solution is acidified and crystallized to obtain high-purity benzoic acid.
4.Wastewater Purification and Resource Recycling
After extraction, the benzoic acid content in the wastewater is significantly reduced, allowing further treatment by biological processes or membrane separation to meet discharge standards. Throughout the entire process, extractant loss is kept below 2%, and the overall resource recovery rate exceeds 95%, demonstrating both economic feasibility and environmental sustainability.
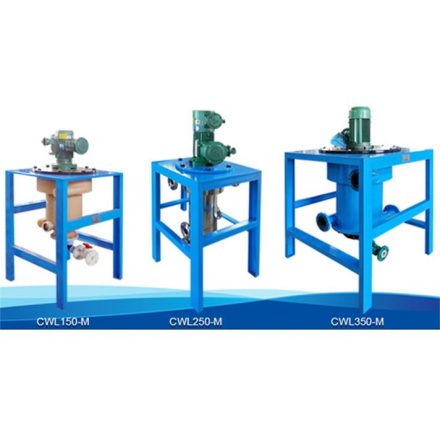
Technical Advantages of the Tiei Extraction CWL-M Centrifugal Extractor
1.High-Efficiency Mass Transfer and Phase Separation
Tiei Extraction CWL-M centrifugal extractor adopts dynamic sealing and variable-frequency speed control, allowing precise regulation of the rotor speed within the range of 800–2000 rpm to accommodate two-phase systems with different viscosities and densities. Its unique dual-stage impeller design reduces the average droplet diameter to 50–100 μm, increasing mass-transfer efficiency by more than 40% compared with conventional equipment. As a result, a single-stage extraction efficiency of up to 98% can be achieved.
2.Modular Design and Intelligent Control
The equipment integrates real-time monitoring of multiple parameters, including flow rate, temperature, and pressure, and automatically adjusts the phase flow ratio and centrifugal field intensity to ensure stable operation. The modular configuration enables rapid disassembly and cleaning, while the processing capacity of a single unit ranges from 0.5 to 50 m³/h, allowing flexible adaptation to production lines of different scales.
3.Corrosion Resistance and Long Service Life
In view of the mildly acidic nature of benzoic acid–containing wastewater, all wetted parts of the centrifugal extractor are fabricated from Hastelloy alloys or coated with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), providing excellent corrosion resistance. With a dynamic balancing accuracy of ISO 1940 G1 grade, the equipment achieves a continuous operating lifetime exceeding 8,000 hours, significantly reducing maintenance requirements and operating costs.
Centrifugal extraction technology provides a reliable route for the efficient recovery of benzoic acid from aqueous systems, while the Tiei Extraction CWL-M centrifugal extractor further enhances the economic feasibility and environmental performance of the process through technological innovation. With the growing market demand for organic acids, centrifugal extraction technology is expected to play an increasingly important role in the field of resource recycling, supporting the industry’s transition toward green and sustainable development.
Email: sales@tieiextraction.com
Whatsapp: +86 19069612820